Aerobic Respiration
Cellular Respiration when Oxygen are present
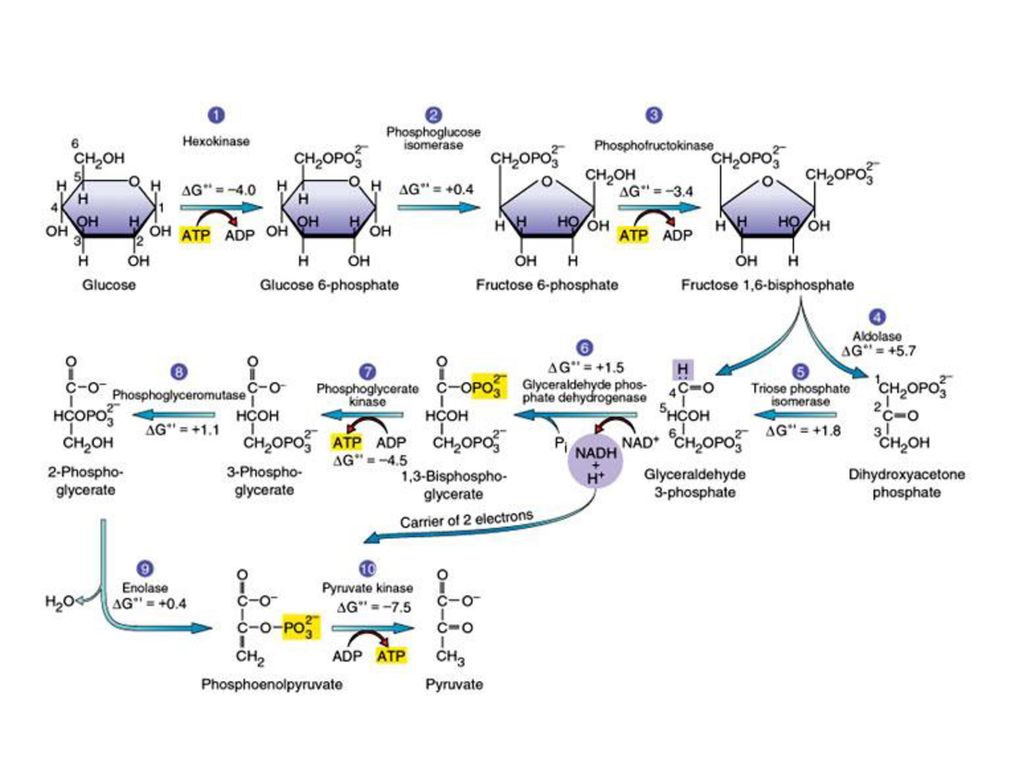
Glycolysis
glucose -> 2Pyruvate + 2H2O
2*ATP -> 2*ADP; 2*NAD+ -> 2*NADH
Splits one 6 carbon sugar into two 3-carbon pyruvate.
The Cleavage reaction happens at step four.
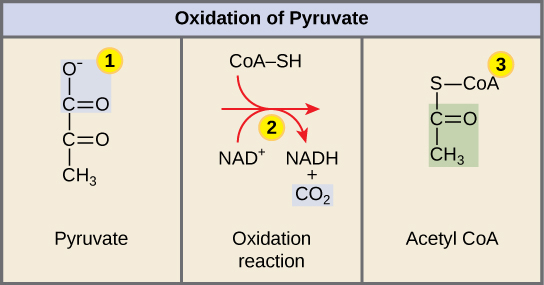
Pyruvate Oxidation
pyruvate -> acetyl CoA;
NAD+ -> NADH
Happens while moving into the mitochondrial matrix
undergoes Decarboxylation->Redox->Addition
Kreb's Cycle
2*Acetyl CoA + 2*CoA + 6*NAD+ + 2*FAD+ + 2*H2O + 2*ADP --> 4*CO2 + 4*CoA + 6*NADH + 2*FADH + 2*ATP
Main source of Energy for cells, provides FADH and NADH for ETC

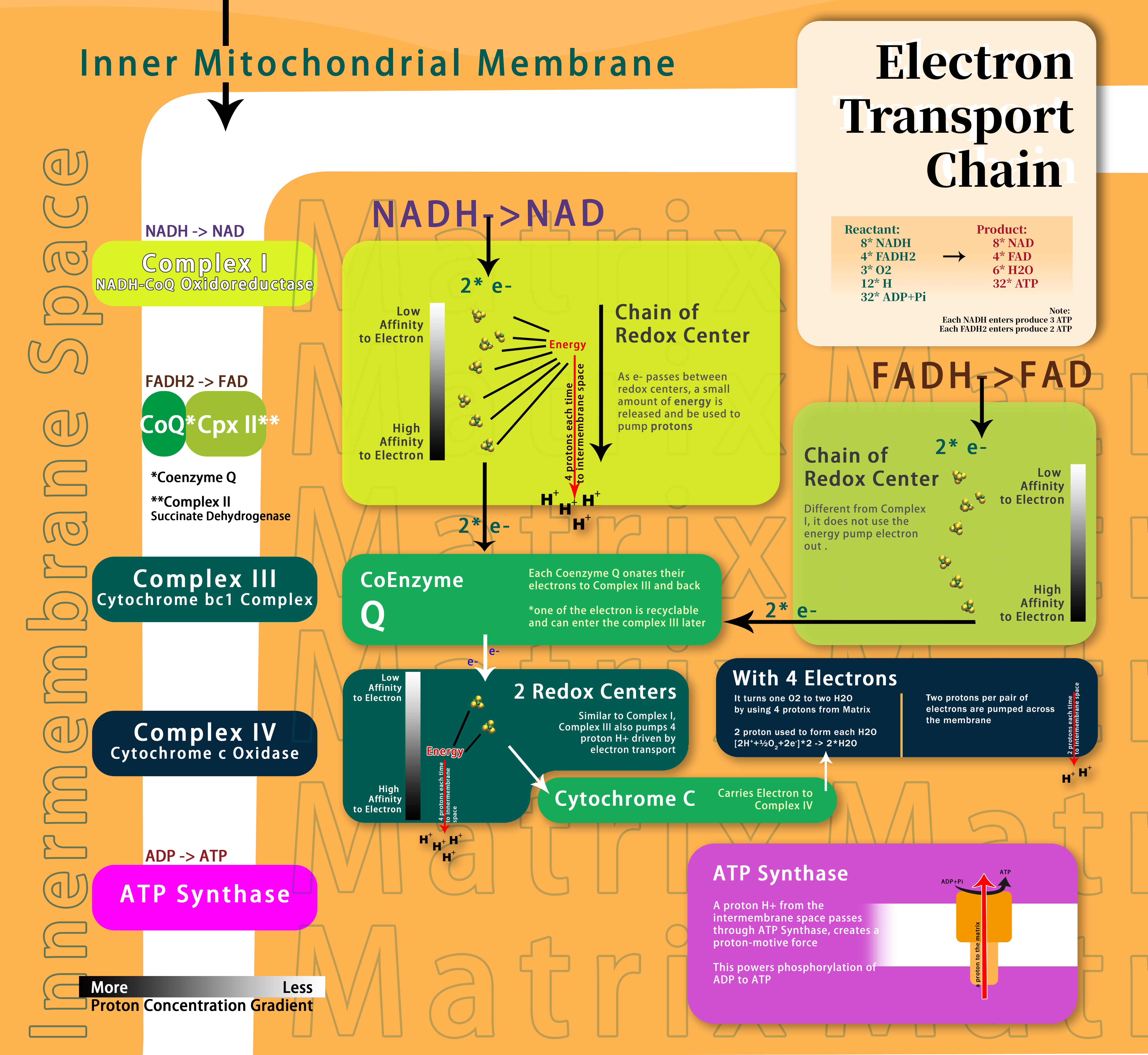
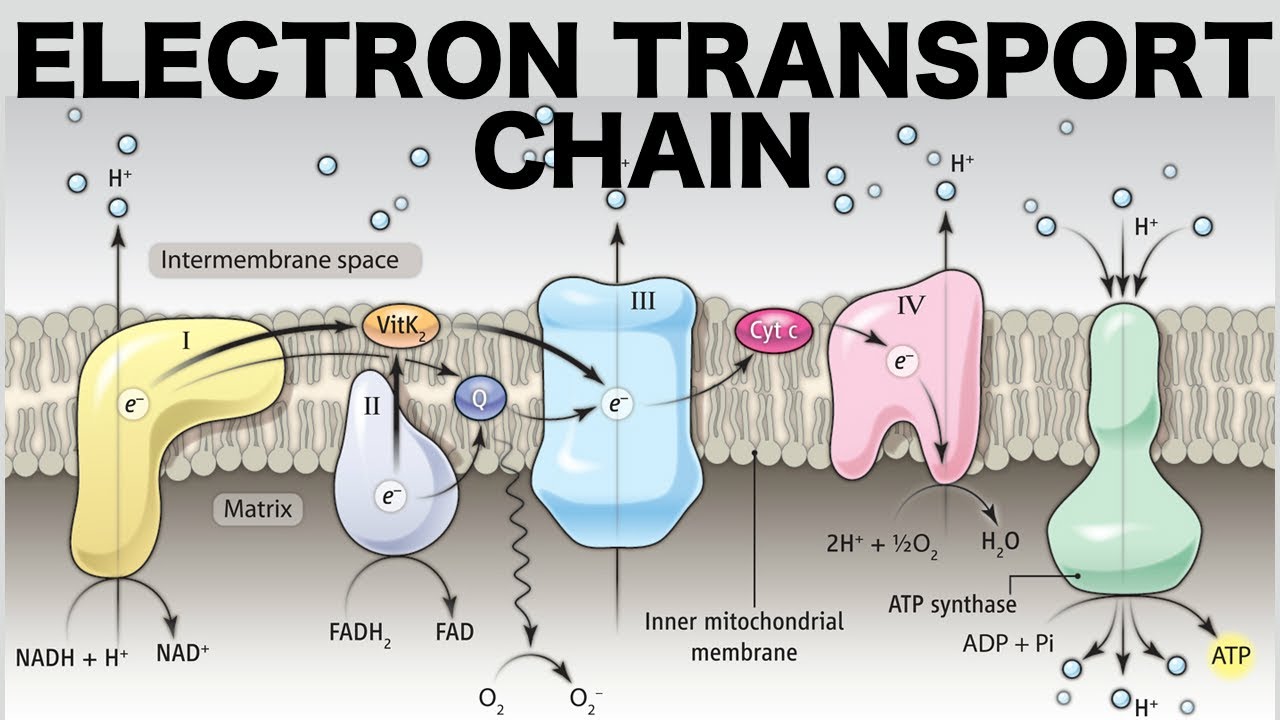
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
8*NADH + 4*FADH2 + 3*O2 + 12*H + 32*ADP + Pi -> 8*NAD + 4*NAD + 6*H2O + 32*ATP
Produces the most ATP. Each NADH produces 3 ATP and each FADH2 produces 2 ATP
Back



